Diaphragm pumps are popular because of their versatility and efficiency. However, they can encounter common issues that require attention. After all, the various industries using it daily rely on its optimal performance.
More importantly, manufacturers understand this better than anyone else. According to an article by Springer Link, the nickel-titanium diaphragm material of modern pumps may improve equipment reliability and efficiency. As technology progresses, pumps could become more resilient to some recurring problems.
Even with the latest additions to diaphragm pumps, there could still be some common issues to watch out for, and below is how to address them:
- Wear And Tear
The diaphragm is a critical component of a diaphragm pump. But how does a diaphragm pump work? It generates the pumping action that moves fluids from one place to another.
Over time, diaphragms can wear out or become damaged. Moreover, this can lead to leaks or reduced performance.
Inspecting diaphragms regularly and replacing them as needed is essential. While they can prevent mechanical issues, high-quality diaphragms made from durable materials can also help extend the lifespan of diaphragm pumps.
- Clogging
Diaphragm pumps can also experience clogging due to the build-up of debris or solids in the pump’s inlet or outlet, like those in a liquid metering pump. It can cause the pump to lose suction or fail to deliver the desired flow rate.
This reduction in flow could put extra strain on the pump motor, leading to eventual failure.
Installing appropriate filters or strainers that can capture debris before it enters the pump is crucial to avoid clogging. Regular cleaning of the filters or strainers can also help prevent further problems.
- Overheating
Diaphragm pumps that feel hotter than usual, radiating excess heat, or causing smoke or water vapor to emanate from them, could be overheating. Along with inadequate functioning, it could also cause component damage, which reduces their lifespan.
Overheating can occur in diaphragm pumps due to the following:
- Excessive use
- Inadequate cooling
- Improper installation
Ensuring the pump installation is well ventilated and the cooling system is correctly functioning can help prevent overheating. In addition, limiting the pump’s use to its recommended duty cycle can prevent overheating issues.
- Making Noises
Although heavy-duty machinery is bound to make some noise, it could go up somewhat if something is wrong. When projects experience downtime, it also means delays. Hence, if unusual noises come from the diaphragm pump, it may be time for a service.
The usual culprit for noisy operations—insufficient oil levels. Therefore, giving the pump a good service and topping up the oil could be all the pump needs. Regular services could thus save workers time and money.
- Erratic Functioning
Pumps could work hard depending on the job it needs to perform—often long hours a day. They could be prone to valve damage or obstruction from this prolonged operation.
The result could lead to erratic functioning. In some instances, a good cleaning could help. In contrast, damage to the internal parts, like the valves, may require professional repair.
- Ball And Seat Failure
A faulty ball and seat often interrupts pump cycles. It could be due to damage from the ball becoming lodged in the seat from excessive pressure. Unfortunately, this is relatively challenging to fix on-site. Professionals may have to step in before the pump can be used again.
- Leaking
As most diaphragm pumps work with liquids, they may eventually spring a leak. However, it is a common issue with diaphragm pumps—albeit preventable. Workers using the pumps could take more care when using them to extend their functioning.
Below are the general causes of leaks and how to avoid them:
- Diaphragm Scratches: High pressure from the fluid intake could leave scratches on the air side where it touches the inner chamber. Two solutions for this problem are lifting the pumps to mitigate the pressure or installing back-pressure devices on the exhaust.
- Stretched Diaphragms: Each pump will have torque values in its user manual. These values are there to protect the pump from damage. Workers operating the pump outside the given guidelines could cause the diaphragm to stretch.
- Warping Or Degradation: Diaphragms exposed to harsh chemicals or warm liquids could quickly lose their functioning. It would be best to check the operating guidelines before using the pump. Using the correct type of pump for the job should prevent damage to the pump and its diaphragm.
- Diaphragm Punctures: Sharp objects could easily puncture the membrane during fluid circulation, especially when the pump needs to clear floodwater containing debris. For this reason, a screen filter on the intake line could catch any debris before it enters the pump chamber.
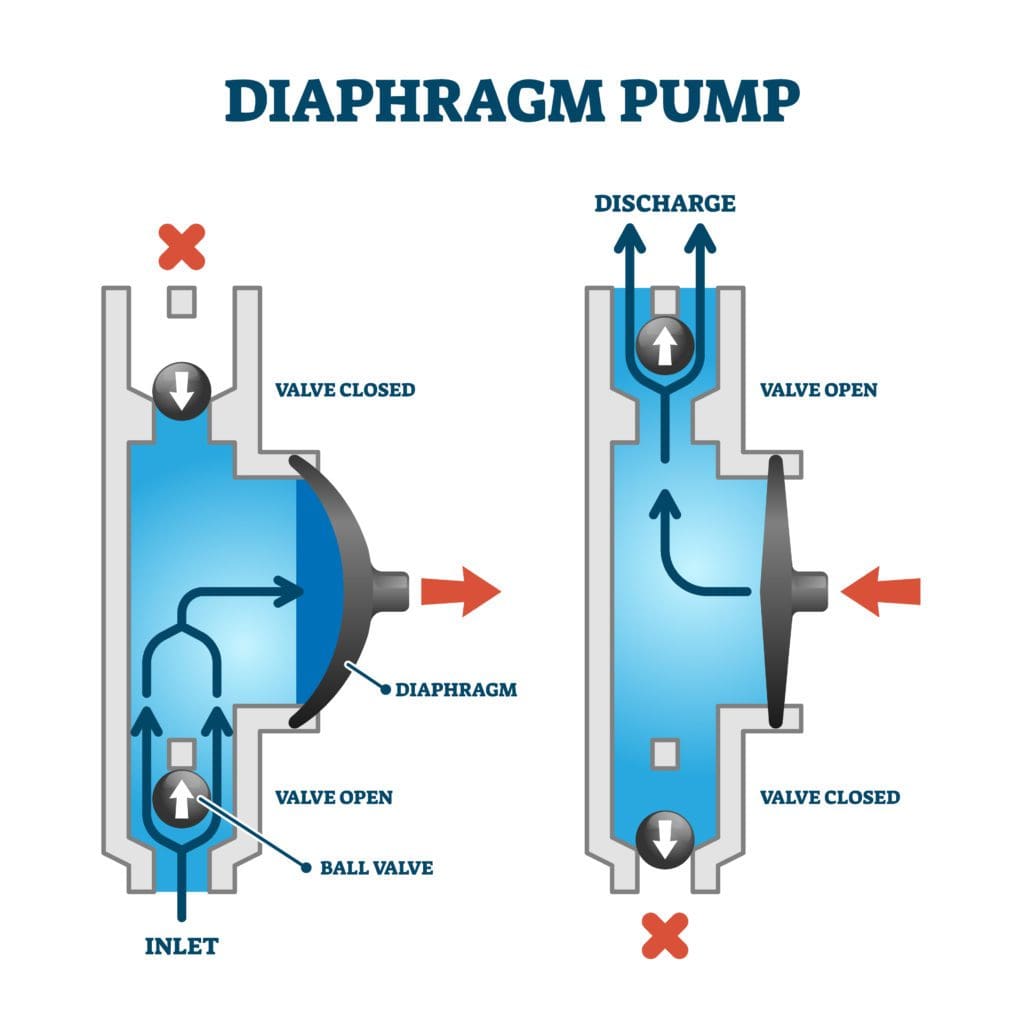
Machinery is bound to cause some problems along the line. But by following recommended operational instructions in the user manuals, workers can stave off critical failure of the diaphragm pumps.
In Conclusion
Diaphragm pumps are reliable and efficient machines that can encounter common issues requiring attention to maintain optimal performance. Regular inspections, appropriate maintenance, and using high-quality components can help prevent and address these issues, ensuring that your diaphragm pump continues to provide reliable performance for years to come.

